Lac Operon (Prokaryotes)
Discovered By: François Jacob and Jacques Monod in 1961
Table of Contents
(1) Genes
Housekeeping genes: “Always cell are on” . Some genes in bacterial cells are important to the life of the cell. Thus their expressions occur constitutively and not subject to regulation.
Inducible gene: “Normally off”. Because it induces or switch on the gene.
Repressible gene: “Normally on”. Because it represses or switches off the gene.
(2) Regulation
Positive Regulation: Activator protein (located near the promoter) binds to the target regulatory site to stimulate transcription (increased rate of transcription).
Negative Regulation: Repressor protein binds to target site and prevents the transcription. Blocks or turns off the expression/transcription ption of genes.
Operon: An operon is a unit of bacterial gene expression and regulation.
Lac Operon: Consists of cis acting structural genes an operator and a promoter, product of lac operon is involved in catabolism of Lactose.
Lac operon codes for enzymes involved is the catabolism of lactose (B-galactoside) that E.coli uses for energy.
Lactose = Glucose + Galactose.
It is an inducible gene, expressed in the presence of inducers (lactose, allolactose).
Structure of Lac Operon:
① Regulatory Gene [Lac I; I-gene]
- Codes for production of Lac repressor protein.
- Has its own promoters. It is a trans acting” regulatory gene,
② Promoter Gene [Lac P; P-Gene]
- Binding site for RNA polymerase.
③ Operator Gene [Lac O; O-gene]
- It is a cis acting site on DNA to which lac repressor binds
- DNA sequence between Promoter and structural gene from-5 to +21
- When lac repressor binds to operation it prevents! RNA polymerase from transcription.”
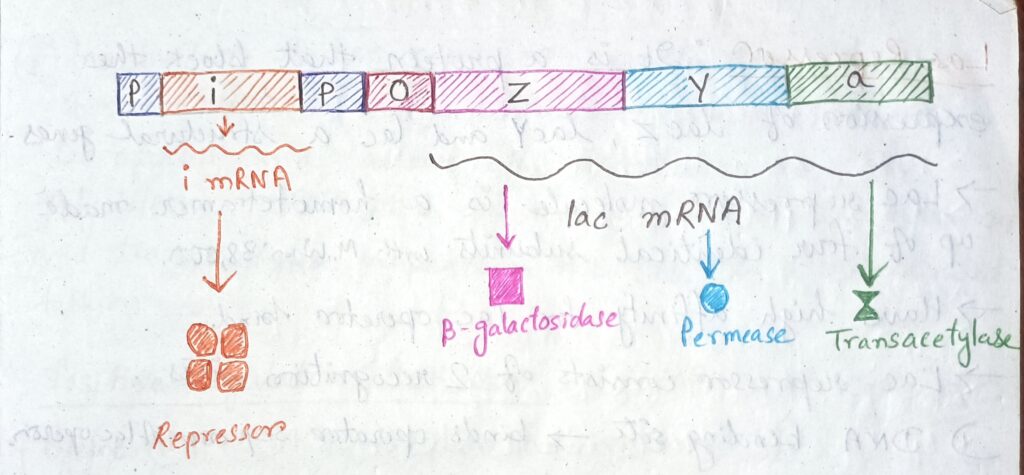
Structural Gene:
ⅰ) Lac Z: Codes for β-galactosidase that cleaves lactose glucose + galactose
Lactose → Allolactose (Lactose isomer)
ii) Lac Y: Codes for β-galactosidase, Permease (found cytoplasmic membrane) helps to transfer lactose from outside to inside of the cell.
iii) Lac A: Codes for β-galactosidase transacetylase. Not essential for lactose metabolism. Role in detoxification by transferring acetyl group from acetyl CoA to β-galactosides.
Lac Repressor:
- It is a protein that block the expression of lac z, lac y and lac a structural genes
- Lac repressor molecule is a homotetramer made up of four identical subunits with M.W~ 38,000.
- Have high affinity for Lac Operator bind.
- Lac repressor consists of 2 recognition sites:
- DNA binding site binds operator sequence of lac operator.
- Allosteric site bind lactose allosteric effectors or inducers.
Regulation of Lac operon :
Negative regulation of Lac Operon
Inactivation of Lac repressor permits the transcription of the structural genes of the lac operon and allows the translation of the polycistronic mRNA, the enzymes B-galactosides, Permeaks and transacetylase, appears in the cell is a coordinated fashion.
Positive Regulator / Activator: C-AMP – CRP Complex. (Cyclic AMP – CAMP receptor Protein complex)
- Stabilizes RNA polymerase.
- The activator protein only works when glucose is absent. CAMP-CRP complex bound to specific base (activation site) in the promoter region.
- CRP dimer binds to ~ 22 bp segment having consequences of Pentameric sequence. (5′-TGTGA-3′)
- CRP introduces a >90° bend Into FOMA at its binding site
