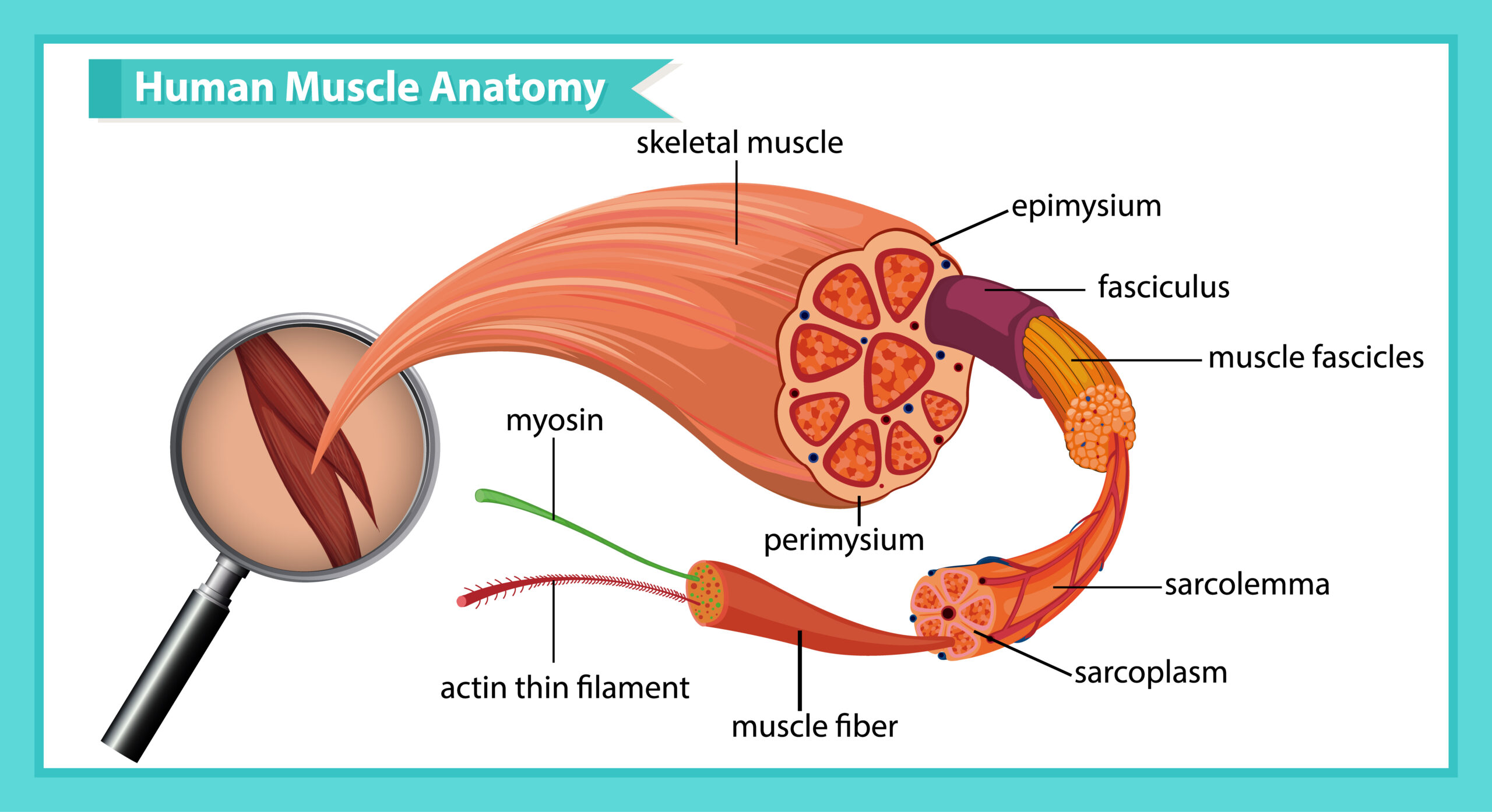
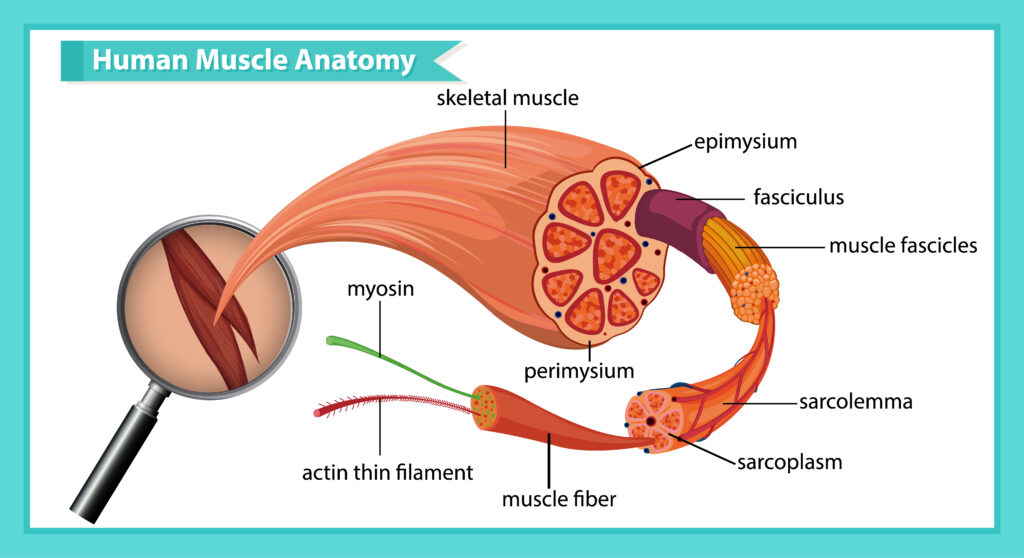
Definition: Spindle shaped fibre like cells having ability to contract in order to produce movement of body parts is called muscle tissue.
Structure:
- Shape: The muscle cells are always elongated, slender and spindle shaped fibre like cells.
- Covering: There is a outer- tissue above the muscle fibres. -covering of connective
- Blood vessels: Blood vessels present in muscle tissue.
- Matrix: There is no matrix in the intracellular. space between the muscle cells.
- Nerves: Muscle tissues are associated with nerves.
Function :
- Movement: Control the movement of organs and body parts, and helps in locomotion.
- Blood circulation: By contraction relaxation of heart, blood circulate throughout the body.
- Producing Heat: Muscle tissues can produce heast in the body.
- Control in Respiration: Control respiration by the respiratory muscle.
Types of Muscle Tissue:
3 types of muscle tissue are there :
- Muscle Tissue
- Smooth Muscle
- Cardiac Muscle
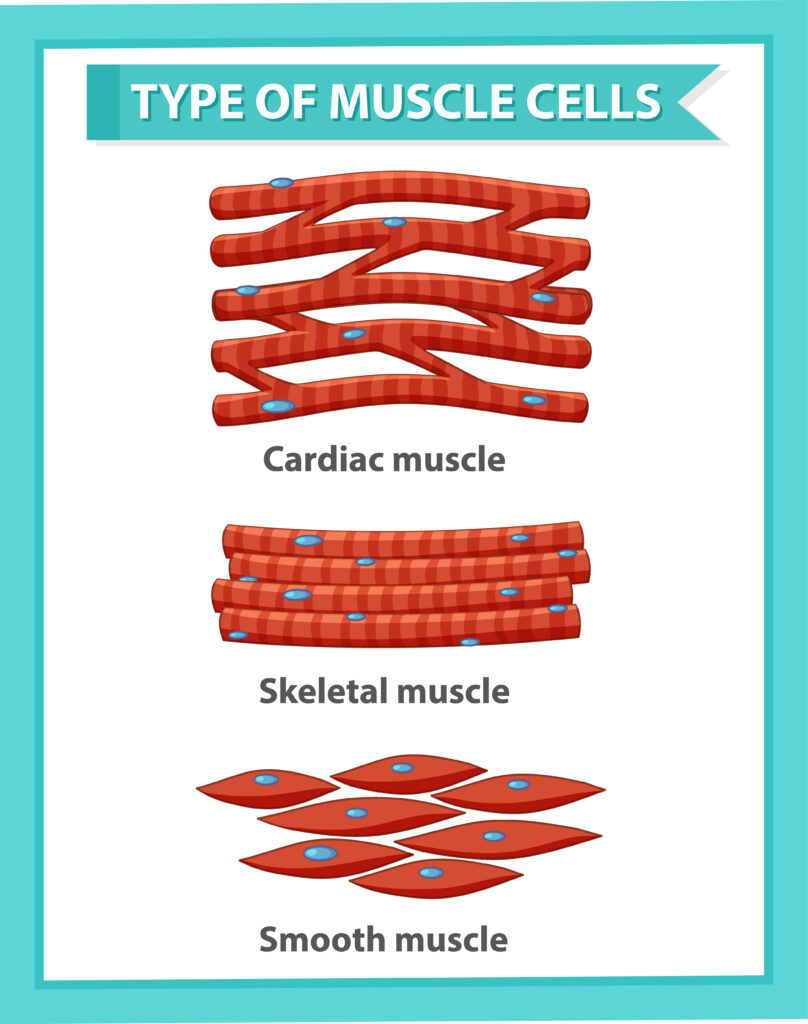
(I) Striated or Skeletal or Voluntary Muscle :
Definition: Long cylindrical, multinucleate cells generally attached with skeleton and voluntary in action is called straited or skeletal muscle.
Location: Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and occasionally to skin.
Structure :
- Shape: Long, cylindrical shaped muscle fibre.
- Nuclei: This tissue is multinucleated.
- Striations There is band or striations muscle fibre on the
Function:
- Shape: It gives the shape of the body.
- Movement: As it is voluntary in action, it helps in movement of body parts according to wish.
- Contraction: It contracts movement very fast helps m
(II) Non-Striated or Involuntary or Smooth Muscle :
Definition: Those muscles controlled by Automatic Nervous System having smooth Involuntary muscle, no bands, they are called non-striated or involuntary muscle.
Location: Blood vessels, Oesophagus, epiglottis, reproductive tracts etc.
Characters :
- Shape: short, spindle shaped with pointed end
- Nuclei: single nucleus present at centre.
- Blood supply: This muscle tissue are with less vascular
Functions:
- Control: It controls the contraction of internal. organs.
- Movement: It helps in movement of internal organ.
(III) Cardiac Muscle :
Definition: Branched, striated, generally uninucleate cells and involuntary muscle action is called cardiac muscle.
Location: The walls of the heart.
Characters:
- Shape: Short, cylindrical with flat ends.
- Striations: There is band or striation on this tissue.
- Action: It is involuntary in action.
Function:
- Blood circulation: As it contracts the heart, it propels blood into the circulation.