Answers of short question from PYQ of Paper Developmental Biology of Semester VI of the years 2020, 2021, 2022 & 2023 respectively.
Developmental Biology 2020
1. Answer any ten questions:
a) Name two Wnt antagonists which act as head inducer ?
Ans→ Chordin and Noggin are the two antagonists that act as a head inducer.
b) What is Nieuwkoop centre?
Ans→ The Nieuwkoop centre is a crucial region in amphibian embryos that determines the body axis and induces the formation of the dorsal structures during early development.
c) What is spermioteleosis?
Ans→ Spermioteleosis is a process where the spermatids transform or modify into mature elongated spermatozoa or sperm cells.
d) What are the secretions of Sertoli cells?
Ans→ Androgen-binding protein (ABP), Inhibin, Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) are the secretions of Sertoli cells.
e) Define blastomere.
Ans→ A blastomere is a single cell formed by the division/cleavage of a fertilized egg (zygote) during early embryonic development.
f) What do you mean microlecithal egg?
Ans→ When the egg contains less or negligible amount of yolk then it is called microlecithal egg.
Example: Eggs of sea urchin, star fish, amphioxus
g) What is corpus albicans?
Ans→ Corpus albicans is a white, fibrous mass, regressed form of corpus luteum in the ovary.
h) What is Golgi rest ?
Ans→ The remaining part of the Golgi apparatus is gradually reduced and ultimately discarded from the sperm regarded as Golgi -rest.
i) Define ectopic pregnancy?
Ans→ When a fertilized egg or blastocyst implants and grows other than uterus, typically in the fallopian tube, ovaries, cervix then it is called ectopic pregnancy.
j) Cell division without growth is_______.
Ans→ Cleavage.
k) Name two hormones that cause the contraction of the uterus.
Ans→ Oxytocin and Prostaglandin
l) The beginning of menstruation is known as_______.
Ans→ Menarche.
m) Which hormone is the basis for pregnancy test?
Ans→ Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
n) What is the fate of blastopores in the case of Tunicates?
Ans→ In tunicates, the blastopore becomes the mouth of the organism during development.
o) What is epiboly?
Ans→ Epiboly is a process in embryonic development where cell layers spread and cover the embryo’s surface as it grows.
2. Answer any five of the following:
a) What is discoidal placenta?
Ans→ A discoidal placenta is a circular-shaped placenta where the villi occurs on a small disc shaped area found in some mammals (rat, rabbit).
b) Why head region of amphibian gastrula does not undergo convergent extension?
Ans→ In amphibian gastrulation, the head region needs to maintain its specific shape & structure to form critical features like brain and sensory organs. Convergent extension elongate and narrow the body axis, facilitating proper tissue organisation. So it’s not crucial for the development of head region.
c) Mention the body parts of Ectodermal and Mesodermal origin.
Ans→ Ectodermal origin: Skin (epidermis, hair follicle, nail); nervous system (brain and spinal cord); cornea of eyes, posterior pituitary gland; pineal gland; adrenal medulla etc.
Mesodermal origin: Skin (dermis region), muscle system; skeletal system; circulatory system; reproductive organs; adrenal cortex etc.
d) What is gray crescent and mention its significance?
Ans→ Grey crescent is a light-grey area along one side of the embryo of an amphibia, formed by the displacement of cortical cytoplasm during fertilization, playing a crucial role in the development of the future dorsal side of the embryo.
Significance: It is crucial for establishing the embryonic axes and subsequent body plan patterning.
e) Write briefly on superficial cleavage.
Ans→ Superficial cleavage is a pattern where cleavage occurs at the cytoplasm around the yolk during early embryonic development.
Example: Superficial cleavage seen insects, frog eggs.
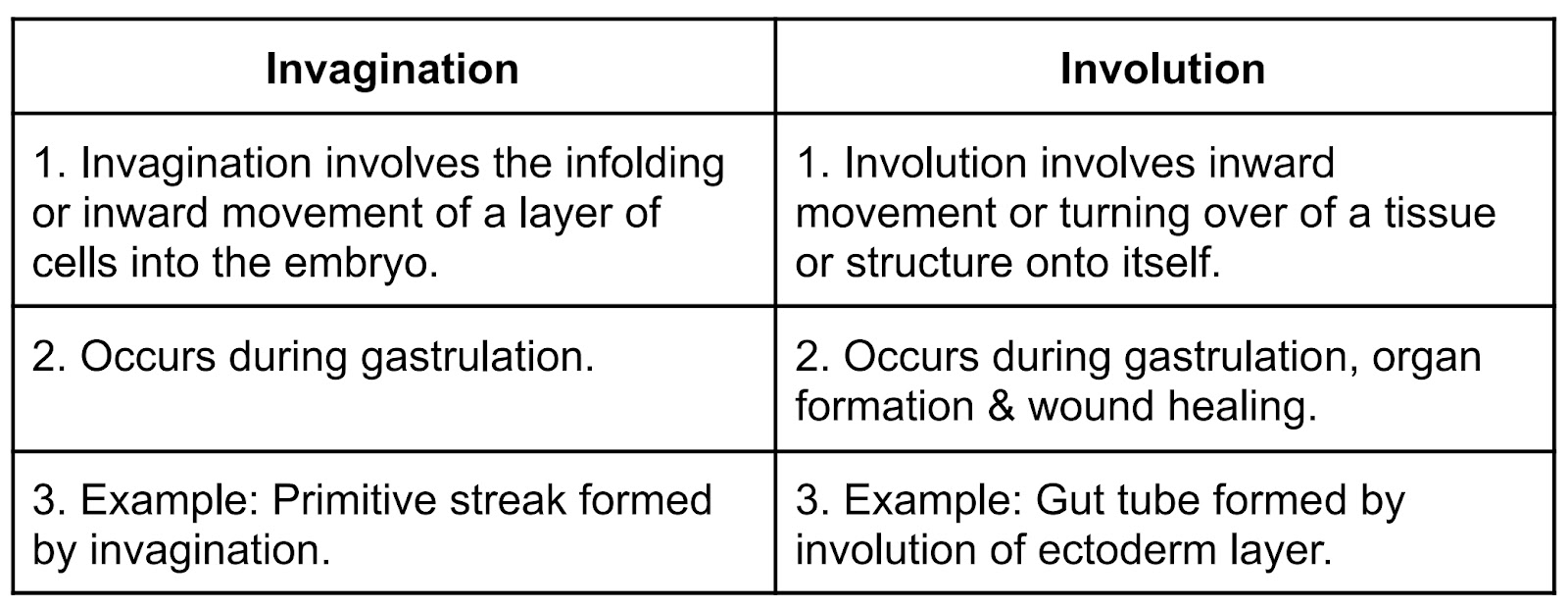
f) Write the difference between invagination ?
Ans→
g) Describe the significance of chemotaxis in fertilization with proper example.
Ans→ Chemotaxis plays a significant role in fertilization by guiding sperm cells towards the egg through chemical signals released by the egg.
In sea urchins, the egg release chemoattractant (speract) which diffuse, into surrounding water and the sperm which are sensitive to speract sense the gradient and get closer and reach the egg, increasing the chances of successful fertilization.
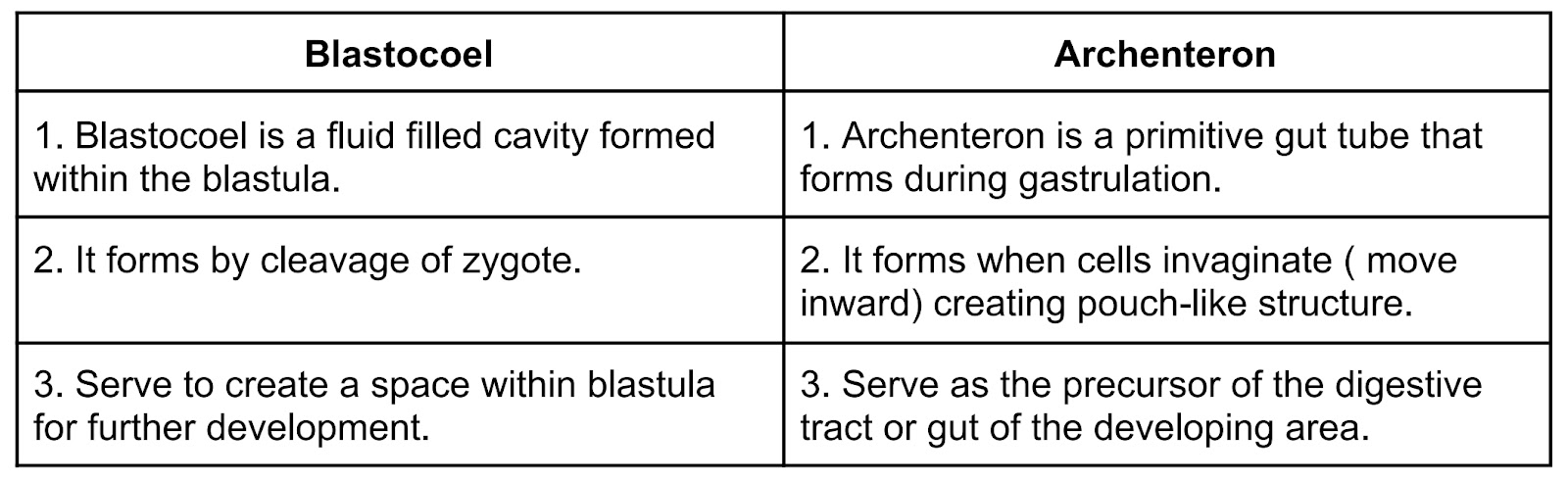
h) What is the difference between blastocol and archenteron.
Ans→
Developmental Biology 2021
1. a) Define embryonic induction?
Ans→ Embryonic induction is the process by which one group of cells influences the development of neighbouring cells, leading to the differentiation of specialized tissues and organs during embryonic development.
b) Which is the first extra embryonic membrane to appear in a chick?
Ans→ Yolk sac
c) State the role of noggin in embryogenesis?
Ans→ Noggin plays a crucial role in promoting somite patterning in developing embryo and regulates bone morphogenic protein 4 (BMP4) during development for proper joint formation.
d) What is polarity of egg?
Ans→ Polarity of egg refers to its organization into distinct region or poles, typically an animal pole (containing nucleus & cytoplasm) and a vegetal pole (containing more yolk).
e) What is compaction?
Ans→ Compaction is the process during early embryonic development where cells in the pre-implantation embryo become tightly packed, forming a compacted mass of cells, helps in establish polarity and differentiation.
f) What is ectopic implantation?
Ans→ Ectopic implantation refers to the implantation of a fertilized egg or blastocyst outside the uterus, typically is fallopian tube, ovaries, cervix or abdominal cavity.
g) Write the role of LH hormone in oogenesis.
Ans→ Luteinizing Hormone (LH) plays a crucial role in oogenesis by stimulating the release of a mature egg (oocyte) from the ovarian follicle.
h) What is resact?
Ans→ Resact is a peptide act as a chemoattractant, release by sea urchin that attracts the sperm towards the egg during fertilization for successful fortilization.
i) What do you mean by discoblastula?
Ans→ Discoblastula is a type of blastula formed due to discoidal cleavage of the zygote forming blastomere over the yolk into two layers – Superficial layer (epiblast) & lower layer (hypoblast).
j) Define regenaration.
Ans→ Regenaration is the process by which organisms replace or restore lost or damaged body parts, tissues, organ through proliferation and differentiation of specialized cells.
k) What is corpus leteum?
Ans→ Corpus leteum is a temporary endocrine structure formed from the graffian follicle in the ovary after ovulation.
l) Define meroblastic cleavage.
Ans→ Meroblastic cleavage is a type of cleavage that occurs in only cytoplasm where yolk is not present during embryonic development incomplete cleavage due to presence of yolk.
m) What is Nieuwkoop center?
Ans→ The Nieuwkoop centre is a crucial region in amphibia embryos that determines the body axis and induces the formation of the dorsal structures during early development.
n) What is Grey crescent area?
Ans→ Grey crescent is a light-grey area along one side of the embryo of an amphibia, formed by the displacement of cortical cytoplasm during fertilization.
o) What is zona pellucida?
Ans→ Zona pellucida is a glycoprotein layer surrounding the plasma membrane of mammalian oocytes.
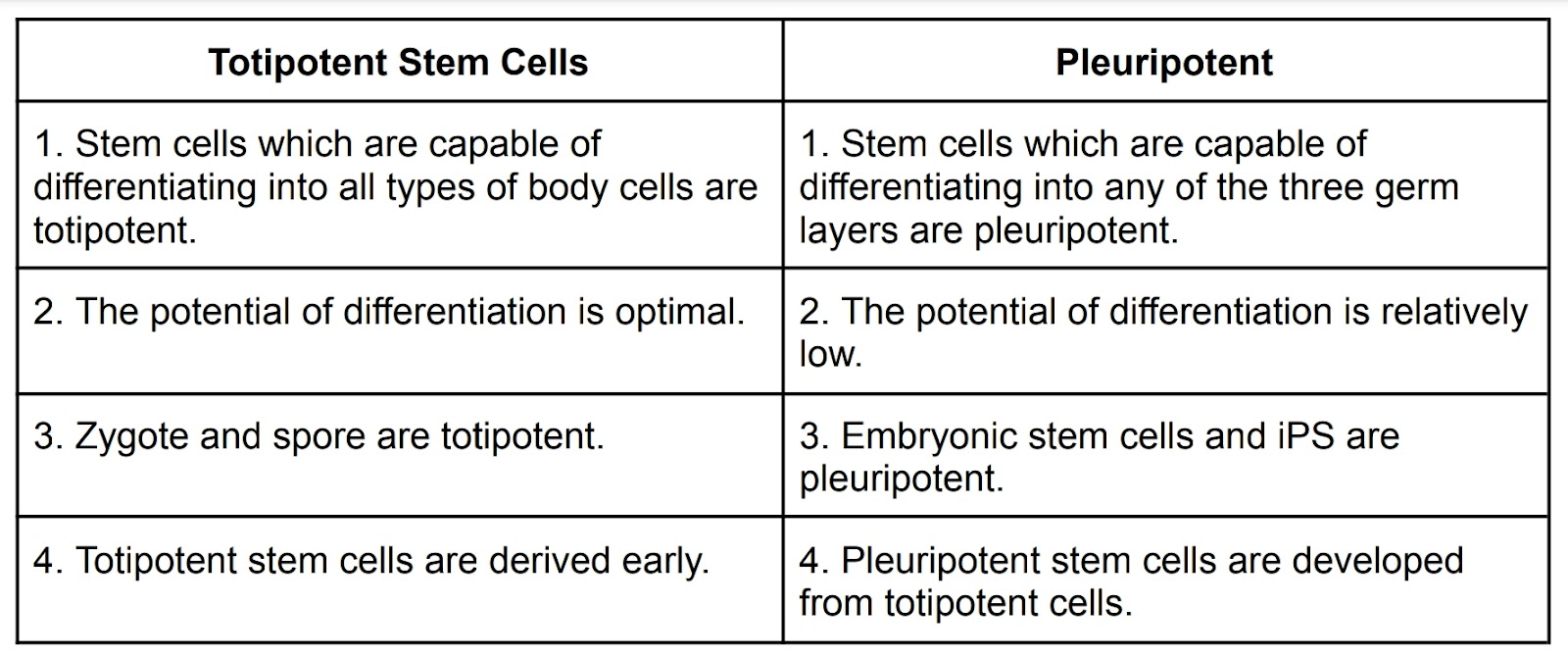
2. a) Distinguish between totipotent and pleuripotent stem cells.
Ans→
b) Differentiate between GIFT and ZIFT.
Ans→

c) State the role of Pax 6 as competence factor in eye development.
Ans→ (i) Initiation of eye development: Pax 6 is one of the earliest genes expressed in developing eyes.
(ii) Regulation of cell differentiation: Pax6 controls the differentiation of progenitor cells into specific cell types. It determines the fate of the cells for formation of eye structures.
(ⅲ) Maintenance of Eye structure: Pax 6 is involved in the maintenance of eye structure and function throughout life.
d) What is amniocentesis ? Mention its significance.
Ans→ Amniocentesis is a prenatal diagnostic procedure to obtain a small sample of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus in the uterus.
Significance: It provides a definitive diagnosis for various genetic disorders, chromosomal abnormalities.
e) Write short note in spermiogenesis.
Ans→ Spermiogenesis is the final stage of spermatogenesis in which spermatids are develop into mature sperm cells or spermatozoa.
In this process, spermatids gradually formed a distinct head containing the condensed nucleus and acrosome, a midpiece containing mitochondria for for energy production and a flagellum for motility.
f) Write down the hormonal control of menstrual cycle.
Ans→ Menstrual Phase: Shedding of uterine lining occurs when decrease in level of oestrogen and progesterone.
Follicular phase: FSH stimulates the development of ovarian follicle.
Ovulation: LH triggers the release of egg from the ovary.
Luteal phase: Corpus luteum forms from ruptured follicle and produces progesterone to prepare the uterine wall.
g) Define capacitation of sperm and mention its significance.
Ans→ Capacitation of sperm is the process where sperm undergo biochemical changes in their membrane structure making them capable of fertilizing an egg.
Significance: Capacitation enables sperm to acquire the necessary motility, membrane changes and biochemical modification needed to penetrate the egg’s protective layers.
h) Write a short note on a block of polyspermy with a diagram.
Ans→ Block of polyspermy refers to the prevention or blocking of multiple sperm to fertilize a single egg.
Developmental Biology 2022
1.a) What do you mean by differentiation?
Ans→ Differentiation refers to the process by which cells become specialized in structure and for specific function during development.
b) What is delamination?
Ans→ Delamination is the process in which layers of tissue or cells separate from each other during embryonic development or tissue formation.
c) What do you mean by the potentiality of a cell?
Ans→ Potentiality of a cell refers to its capacity to differentiate into various cell types or to give rise to different cell lineages during development.
d) Name two wat antagonists which act as a head inducer?
Ans→Chordin and noggin
e) Define golgi rest.
Ans→ The remaining part of the Golgi apparatus is gradually reduced and ultimately discarded from the sperm regarded as Golgi -rest.
f) Which type of egg is related to superficial cleavage? Give example.
Ans→ Centrolecithal eggs.
Example: Insects
g) Why cortical vesicles are significant during polyspermy blocking?
Ans→ Because cortical granules form cortical vesicles are released, forming a fertilization envelope which hardens the zona pellucida. This prevents other sperm from entering the egg, thereby playing an important role in polyspermy.
h) What is cephalic flexure?
Ans→ Cephalic flexure is the curvature on bend in the developing embryonic brain that distinguishes the forebrain and midbrain region during early neural development.
i) Write down the function of ZP protein.
Ans– ZP3 protein acts as sperm receptor, facilitating the binding site and recognition of sperm to the zona pellucida of surrounding the egg.
j) Name two teratogenic agents.
Ans→ Thalidomide, alcohol.
k) State the role of the resact molecule in sea urchin fertilization.
Ans→ Resact is a peptide molecule act as a chemoattractant, release by the egg of sea urchin that attracts the sperm towards the egg during fertilization for successful fertilization.
I) What is Nieuwkoop centre?
Ans→ The Nieuwkoop centre is a crucial region in amphibia embryos that determines the body axis and induces the formation of the dorsal structures during early development.
m) Define capacitation.
Ans–> Capacitation is the process where sperm undergo biochemical changes in their membrane structure making them capable of fertilizing an egg.
n) What is cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast?
Ans→ Cytotrophoblast is a layer of cells in the placenta that contributes to the formation of the chorionic villi.
Syncytiotrophoblast is a layer of multinucleated cells in the placenta that helps in implantation of the egg in the wall of the uterus.
o) What is a hemochorial placenta?
Ans→ Hemochorial placenta is a type of placenta where maternal blood comes in contact with foetal chorion, allowing efficient exchange of nutrients and waste products.
2.a) What do you mean by head and tail organizers?
Ans–> Head organizers refers to a region or group of cells that signals and orchestrates the development of structures in the head region of embryo, including the brain and sensory organs.
‘Tail organizer” refers to a region that develop the structures in the posterior end of the embryo such as tail.
b) Why is oogenesis a wasteful process?
Ans→ Oogenesis is considered as a wasteful process. because it involves the production of a single egg cell. from a single precursor cell through a series of divisions. During this process, many potential egg cell undergo degeneration and are not utilised for fertilization.
c) Write down the role of Ca²+ in egg activation.
Ans→ (i) Ca²+ signalling triggers various metabolic processes within the egg which is necessary for early embryonic development.
(ii) Ca²+ release causes changes in the egg’s membrane potential and structure leading to the prevention of polyspermy.
(iii) Ca²+ is essential for activation of embryonic development pathways, fusion of genetic material, initiation of cell division, cell polarity.
d) Draw and breifly describe the neural tube formation in chick embryo.
Ans→ In chick embryo development, neural tube formation begins with the inward folding of ectoderm along the dorsal midline of the embryo to form the neural plate. The edges of the neural plate then elevate and fuse creating neural tube give rise to CNS including brain & spinal card.
e) Describe the hormonal control of follicular stage of the menstrual cycle.
Ans→ During the folicular stage of the menstrual cycle, the pituitary gland release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) which stimulates the growth and development the ovaries. of follicles in
f) State the major functions of organizer.
Ans→ (i) Induce differentiation: The organizer emits signals that induce neighbouring cells to differentiate into specific structures.
(ⅱ) Patterning and Axis formation: It helps in the formation of body axes, such as the anterior-posterion and dorso-ventual anes.
(iii) Cell fate determination: Influence the fate of nearby cell
(iv) Initiation of signalling Pathway: Initiates and coordinates Various g) State imalling thewayo peroties frowth factors and transcription factors important properties of stem cells.
g) State important properties of stem cells.
Ans→ (i) Self-renewal: Stem cell can replicate themselves through cell division, maintaining an indifferentiated state while also producing specialized cell types.
(ii) Pluripotency or Multipotency: Stem cells possess the ability to differentiate into multiple call types.
(iii) Surescence or Dormancy: Stem cells can exist in a quiescent state, remaining dormant until activated by signals to proliferate.
(iv) Capacity for tissue Regenaration: Stem cells have the potential to replace damaged or diseased cells and tissues.
h) Differentiate between GIFT and ZIFT.
Ans→

Developmental Biology 2023
1.a) What is placenta vera?
Ans→ Placenta vera refers to a condition where the placenta attaches directly to the uterine wall, without any intervening layers.
b) What do you mean by fertilization cone?
Ans→ A fertilisation cone is a specialised structure formed by cortical granule reaction after fertilisation in eggs of certain species such sea urchin or amphibia.
c) What do you mean by macrolecithal egg?
Ans→ A macrolecithal egg is a large egg with a high concentration of yolk, typically foundin eggs of birds, reptiles providing nutrients for the developing embryo.
d) What is corpus albicans?
Ans→ Corpus albicans is a temporary structure in the ovary from the degeneration of the corpus luteum after ovulation.
e) Name two hormones that cause contraction of the uterus?
Ans→ Oxytocin and prostaglandin
f) What is regeneration?
Ans→ Regenaration is the process by which organisms replace or restore lost or damaged body parts, tissues, organ through proliferation and differentiation of specialized cells.
g) Which hormone is the basis for pregnancy test?
Ans→ hCG (Human chorionic gonadotropin)
h) What is spermatid metamorphosis?
Ans→ Spermatid metamorphosis refers to the process by which spermatids mature into spermatozoa (sperm cells) within testes.
i) What is blastodisc?
Ans→ Blastodisc is a disc shaped structure of cytoplasm at the upper surface of york formed by discoidal cleavage during the blastulation process.
j) What do you mean by In Vitro fertilization?
Ans→ In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a medical procedure where an egg is fertilised by sperm outside the body, in a laboratory setting to establish pregnancy.
k) Define ectopic pregnancy.
Ans→ When a fertilized egg or blastocyst implants and grows other than uterus, typically in the fallopian tube, ovaries, cervix then it is called ectopic pregnancy.
l) Mention the role of Sertoli cells is spermatogenesis.
Ans→ Sertoli cells support and nourish developing sperm cells and regulate the process of spermatogenesis within the seminiferous tubule.
m) What is Nieuwkoop center?
Ans→ The Nieuwkoop centre is a crucial region in amphibian embryos that determines the body axis and induces the formation of the dorsal structures during early development
n) Define capacitation.
Ans→ Capacitation of sperm is the process where sperm undergo biochemical changes in their membrane structure making them capable of fertilizing an egg.
o) What is yolk plug?
Ans→ The yolk plug is a dense mass of yolk material that Seals the opening (blastopore) during early embryonic development in amphibians.
2.a) What is periblast? Write down its function.
Ans→ The periblast is a layer of cytoplasm surrounding the yolk in certain eggs, especially in fish, which helps in nutrient distribution during early embryonic development.
Function:The periblast facilitates nutrient distribution to the developing embryo.
b) State the function of Allantois in chick.
Ans→
- Gas Exchange: Facilitates the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the embryo and the environment.
- Waste Storage: Stores nitrogenous wastes like uric acid produced by the embryo.
- Nutrient Absorption: Absorbs calcium from the eggshell to support bone development.
c) What do you mean by Zonary Placenta? Give an example.
Ans→ Zonary placenta is a type of placenta in which the exchange of nutrients, gases, and wastes between the mother and foetus occurs in a belt-like region surrounding the middle of the placenta.
Example: Carnivores like cats and dogs.
d) State the difference between epimorphosis and morphallaxis.
Ans→
| Points | Epimorphosis | Morphallaxis |
| 1. Involvement | Involves significant cell division and proliferation. | Involves reorganisation and differentiation of existing cells. |
| 2. Regeneration site | New tissue forms at the site of injury i.e regeneration. | Little to no cell proliferation; relies on the transformation of existing cells. |
| 3. Example | Limb regeneration in amphibians. | Regeneration in hydra. |
e) What is grey crescent and mention its significance.
Ans→ Grey crescent is a light-grey area along one side of the embryo of an amphibia, formed by the displacement of cortical cytoplasm during fertilization, playing a crucial role in the development of the future dorsal side of the embryo.
Significance: It is crucial for establishing the embryonic axes and subsequent body plan patterning.
f) Write the difference between invagination and involution.
Ans→
| Invagination | Involution |
| 1. Invagination involves the infolding or inward movement of a layer of cells into the embryo. | 1. Involution involves inward movement or turning over of a tissue or structure onto itself. |
| 2. Occurs during gastrulation. | 2. Occurs during gastrulation, organ formation & wound healing. |
| 3. Example: Primitive streak formed by invagination. | 3. Example: Gut tube formed by involution of ectoderm layer. |
g) Write down the role of Ca++ in egg activation.
Ans→ (i) Ca²+ signalling triggers various metabolic processes within the egg which is necessary for early embryonic development.
(ii) Ca²+ release causes changes in the egg’s membrane potential and structure leading to the prevention of polyspermy.
(iii) Ca²+ is essential for activation of embryonic development pathways, fusion of genetic material, initiation of cell division, cell polarity.
h) Write two functions of ZP3 protein.
Ans→ Sperm Binding: ZP3 acts as a receptor for sperm, facilitating sperm binding to the egg’s zona pellucida.
Acrosome Reaction Induction: Triggers the acrosome reaction in the sperm, which is essential for the sperm to penetrate into the egg.

2 thoughts on “Developmental Biology Shorts PYQ”