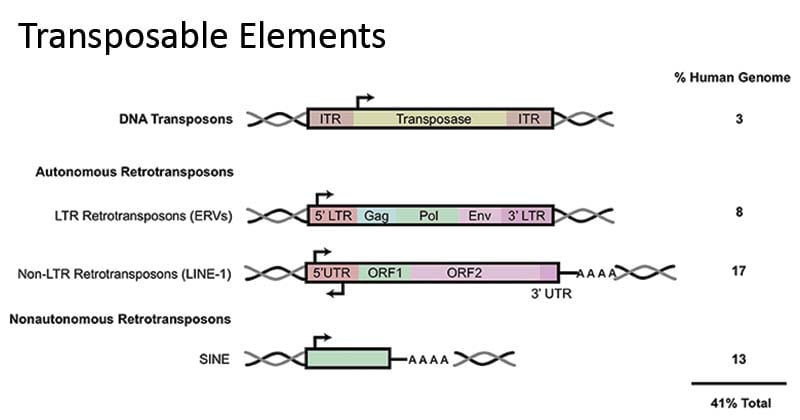
A transposon, also known as a “jumping gene,” is a segment of DNA that can move or “transpose” itself to different positions within the genome of a single cell. This ability to change positions makes transposons significant contributors to genetic diversity and evolution.
Table of Contents
Features of Transposons:
Also Known as: Jumping gene or Mobile elements.
• Can move from one place to another within the genome
First discovered by McClintock in 1940 (Corn/Maize-Colour variation in kernel)
Transposon: Transposon is a DNA sequence that is able to move or insert itself at a new location in the genome.
Transposition: The phenomenon of movement of a transposon to a new site in the genome is referred to as transposition.
Transposase Enzyme: Transposons encode a special protein named as transposase enzyme which o catalyzes the process of transposition.

Cut and paste Transposons
They transpose by excision (cutting) of the transposable sequence from one position in the genome and its insertion to another position within the genome.
Cut and paste transposition involves two transposase subunits.
Copy and paste Transposons:
The process involves the transcription of transposable DNA to produce an RNA intermediate then the synthesis of DNA by reverse transcriptase to form a copy of the transposable DNA. This copy of transposable DNA is inserted to another position within the genome.
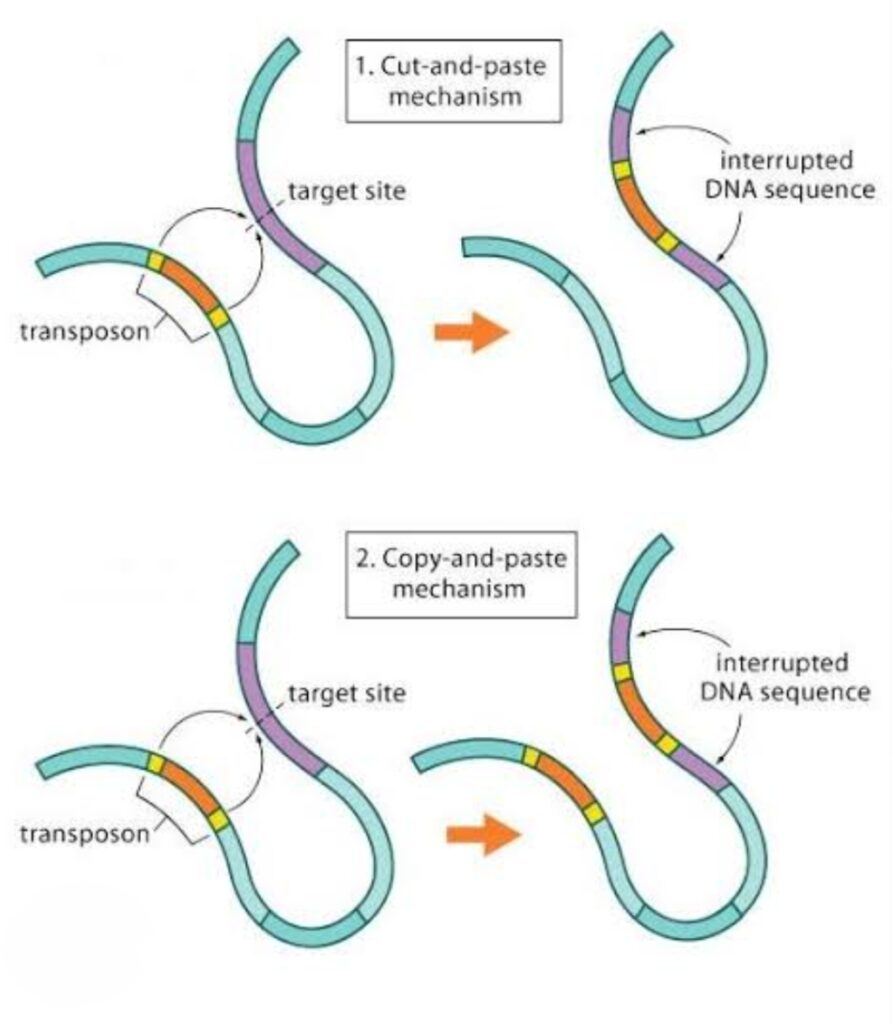
DNA Transposon
IS Element (Insertional Sequence Elements) :
- Type of cut and paste type transposons.
- IS elements are relatively short 2500 bp long.
- They possess ITR (Inverted Terminal Repeat).
- ITR Implies that the sequence at 5′ end of one strand is identical to the sequence at 5′ end of the other strand but they run in inverse opposite direction.
- IS elements encode a protein – Transposase needed for transposition.
Example: IS1 (E.coli chromosome), IS2, IS3 (F plasmid)
P Element :
• P elements are transposable elements found in the genome of fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster).
- P elements are about 2.3kb to 2.9 Kb long.
- Have Inverted Terminal sequence repeats (ITR) at their ends.
- They contain genes encoding-Transposase enzymes.
- Transposition Mechanism – cut and paste type.The transposase enzyme recognizes the ITRs, excises the P element from its original location and inserts it into a new genomic site.
- P elements are responsible for – Hybrid dysgenesis in fruit flies.
A cross between Male with active P elements and a female lacking them leads to genetic instability to form – hybrid dysgenesis (sterile offspring).
Example:
- Male: P element present
- Female: M strain (Normal) have no repression to stop the action of P element
- Produce –> Sterile offspring (Hybrid dysgenesis).
Retrotransposon :
Transposable element in Human DNA 44%
- → 8% retrovirus like elements
- → 33% retroposons
- → 3% Cut and paste transposons.
Most abundant mobile elements in mammals – Retrotransposons that lack LTRS, sometimes called non-viral retrotransposons.
These moderately repeated DNA sequences form two classes in Mammalian genomes – LINES and SINES.
LINEs :
Definition: LINES are autonomous, long transposable elements (non-LTR Retroposon) that move within the genome by copy and paste mechanism encoding their own transposase enzyme.
- Long transposable elements about 6 Kb long.
- Autonomous transposons, meaning they encode their own transposase enzyme required for transposition.
- LINEs transpose through a copy and paste mechanism.
- 21% of total human DNA.
- Contain two Open Reading Frames (ORFS)
–> ORF 1 (1kb long): Encode RNA binding protein
–> ORF 2 (4kblong): Encode Reverse transcriptase enzyme & DNA nuclease
Example: L1, L2, L3 activity protein.
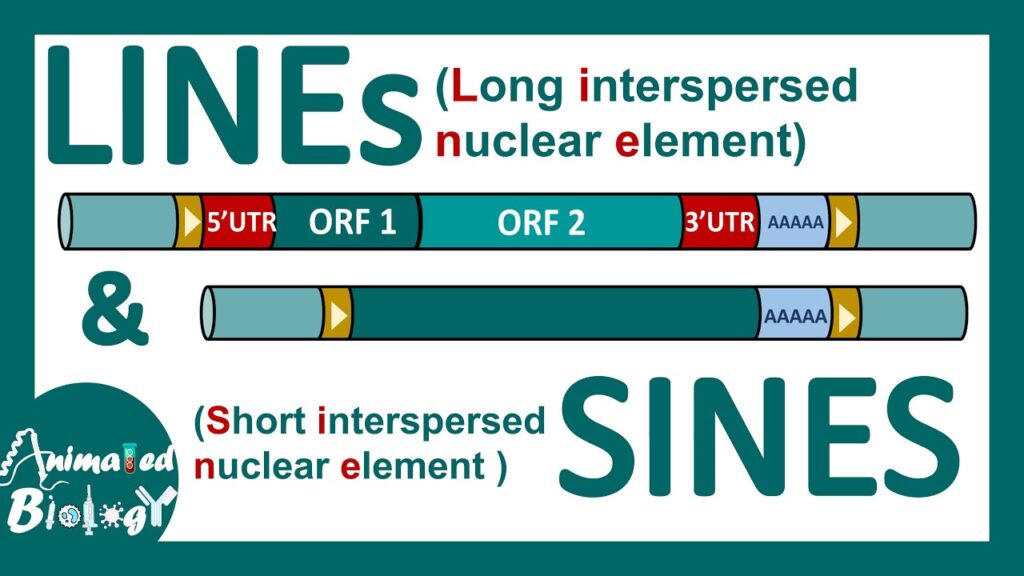
SINEs :
Definition: SINEs are non-autonomous, short transposable elements (non-LTR Retrotransposon) that rely on the enzymatic machinery of LINES for their transposition present in the human genome.
- Small transposable elements – 300 bp.
- SINES are non autonomous, they are dependent on the activity of LINES, for transposition.
- Copy and paste mechanism.
- 13% of total human DNA.
- Non-LTR Retrotransposon (non-viral retrotransposon)
- Do not encode any protein.
- SINES have a single recognition site for restriction enzyme Alu I comprises Alu elements.
Alu Element:
• Alu elements are non-autonomous, short transposable elements (type of SINE) found in the human genome that rely on other elements (LINES) for their transposition.
- 10% of total DNA
- Alu elements are believed to have originated from 7 SL RNA, a component of the signal recognition particle (SRP) involved in protein targeting within cells.
- They can cause genetic rearrangements through non-allelic homologous recombination.
