Answers of short question from PYQ Paper Immunology of Semester IV of the years 2019, 2021, 2022 & 2023 respectively.
Table of Contents
Immunology Paper 2019
1.a) State the characteristics of thymus independent antigens.
Ans→ (i) They are immunogen that can stimulate B cells to synthesize antibodies without the help of T cells.
(ii) These antigens are less complex than thymus dependent antigens.
b) State the function of CRP.
Ans→C-Reactive protein
(i) Activates complement system
(ii) Binds to fc receptor and acts as an opsonin for various pathogens.
c) What is epitope?
Ans→ Epitope is the part of an antigen that binds to an antibody combining site for a specific T cell surface receptor.
d) What is diapedesis?
Ans→ It is a process of extravasation of leukocytes from blood vessels to sites of tissue damage, infection or inflammation.
e) What do you mean by complementarity determining region.
Ans→ CDR are part of the variable chain in Ig (antibodies) and T cell receptors, generated by B cell and T cell respectively, where the antigen these molecules bind to their specific antigen provide a specific antigen recognition site.
f) State the result of treatment of an IgG molecule with mercaptoethanol.
Ans→ A significant reduction of their capacity to induce cytotoxicity of lymphocytes against the respective An-Ab complex.
g) State four cardinal signs of inflammation.
Ans–>The four cardinal signs of inflammation are:-
- i) Rubor (Redness).
- ii) Calor (Warmth) (Heat)
- iii) Tumor (Swelling)
- iv) Dolor (Pain)
h) What is an immunogen?
Ans→ Antigen molecules whicj are able to induce an immune response on the body are called immunogens.
i) What is active immunization?
Ans→ Active immunization stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies against a particular infectious disease.
j) What is recombinant vaccine?
Ans→ A recombinant vaccine is a type of vaccine that uses genetically engineered components from a pathogen into another organism, to stimulate an immune response without causing disease.
k) What is MHC test?
Ans→ It is a histocompatibility antigen blood test that looks at the presence of a protein called Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA).
l) State the role of histamine?
Ans→ (i) Causing allergic and anaphylactic systems.
(ii) Regulate the vasodilation in the body.
(m) State the principle of Mantoux tuberculin skin test?
Ans→ The Mantoux tuberculin skin test works by injecting a small amount of tuberculin purified protein derivative (PPD) into the skin. If a person has been exposed to the bacteria that cause tuberculosis, their immune system reacts, causing a localized swelling at the injection site.
n) State the function of a chemokine.
Ans→(i) Perform cell attraction (Chemotaxis) between the cells.
(ii) Responsible for recruiting leukocytes to inflammatory lesions.
o) State the significance of hybridoma technology.
Ans→ Hybridoma technology is a well established method to produce monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) specific to antigen of interest.
2.a) What do you mean by ADCC? Ans→ ADCC or Antibody dependent, cellular cytotoxicity is a cytotoxic reaction in which the fe receptor bearing Killer cells recognize target cells through/via specific antibodies.
b) What do you mean by secondary lymphoid organs? Give examples.
Ans→ Secondary lymphoid organs are sites where immune responses occur after activation in primary lymphoid organs.
Example: Spleen, lymph nodes
c) State the salient features of immune adaptive immunity.
Ans→ Each adaptive immune cells has a specific receptor.
Each receptor recognizes an antigen which is onto any molecule that may bind TCR.
d) What is acute phase proteins? Give examples.
Ans→ Acute phase proteins are the class of proteins whose concentration in the blood stream either increases or decreases in response to inflammation.
Example: C Reactive Protein, α-acid glycoprotein, haptoglobin.
e) What is Type II Hypersensitivity? Give an example.
Ans→ Type II hypersensitivity reaction is an antibody mediated immune reaction in which IgM or IgG antibodies are directed against the target cell by killing, functional loss or tissue damage.
Example: Hemolytic anaemia
f) What is cytokine pleiotropy? Give example.
Ans→ Cytokine pleiotropy is the ability of a cytokine to produce different types of immune response on different target cells.
Example : Interleukin (IL)
g) State the properties of B cell-epitopes.
Ans→ Properties of B cell epitopes are hydrophilic surface accessibility, Beta turns, exposed surface, polarity and antigen.
h) Describe the concept of clonal selection.
Ans→ Clonal selection is a theory of naive lymphocytes entering the bloodstream, only those exposed by binding antigen on the receptor are able to stimulate to proliferate into effector cells. Upon binding The antigen Lymphocytes become activated and divide and make clones of themselves.
Immunology Paper 2021
1.a) What is TLR?
Ans→ TLR or Toll Like Receptors are an important family of receptors that constitute the first line of defence system against microbes. They can recognize both invading pathogen and molecules released from dying cells and damaged tissues and play a key role to linking innate and adaptive immunity
b) What is paratope?
Ans→ Paratope is the antigen binding site which is the part of the antibody which recognizes and binds antigen.
c) State the function of chemokine?
Ans→ Chemokine activates and attracts leucocytes in the site of injury.
It also transmits signals through receptors.
d) Define Herd immunity?
Ans→Herd immunity/Population Immunity is the direct protection from an infectious disease that happens when a population is immune, either through vaccination or immunity developed through previous infection.
e) What is attenuated vaccine?
Ans→ Attenuated vaccine is vaccine containing live pathogens either reducing the virulences or weakened but retaining their ability to provoke an immune response.
f) Give example of two secondary lymphoid organs?
Ans→ Spleen and Lymph node.
g) Give example of Type I hypersensitivity?
Ans→Atopic disease like allergy, asthma, rhinitis, conjunctivitis and dermatitis.
h) State the principle of Mantoux tuberclin skin test.
Ans→ The Mantoux tuberculin skin test works by injecting a small amount of tuberculin purified protein derivative (PPD) into the skin. If a person has been exposed to the bacteria that cause tuberculosis, their immune system reacts, causing a localized swelling at the injection site.
ⅰ) What is the function of NK cells?
Ans→ (i) Kill virus infected cells and some tumour cells and produce cytokines.
j) Why adjuvants are added to vaccine?
Ans→ Adjuvants are substances used in some vaccines that help in creating a strong immune response in people receiving the vaccine.
k) State the result of treatment of lgG molecules with mercaptoethanol.
Ans→ A significant reduction of their capacity to induce cytotoxicity of lymphocytes against the respective An-Ab complex.
ⅰ) What is the function of hinge region in antibody?
Ans→Connects the Fab and Fc portion.
Provide segmental flexibility which is essential for normal functioning of antibodies; it changes the shape of the antibody.
m) Expand HLA.
Ans→HLA: Human Leukocyte Antigen – are genes in MHC present in chromosome 6 of a human.
n) What is macrophage?
Ans→ Macrophages are phagocytic cells that are matured form of monocytes, killing by engulfing the target cells.
o) What do you mean by ADCC ?
Ans→ Antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) is a cytotoxic reaction mediated by non-immune cells (effector cells) against target cells via non-phagocytic mechanism.
2.a) Explain class switching.
Ans→ Class switching: The process by which a B cell can express a new heavy chain isotype without altering the specificity of the antibody production. This occurs by gene rearrangement.
b) State the four cardinal sign of inflammation.
Ans→ The four cardinal signs of Inflammation are :-
- i) Rubor (Redness).
- ii) Calor (Warmth) (Heat)
- iii) Tumor (Swelling)
- iv) Dolor (Pain)
c) Write down two basic differences between MHC l and MHC II.
Ans→
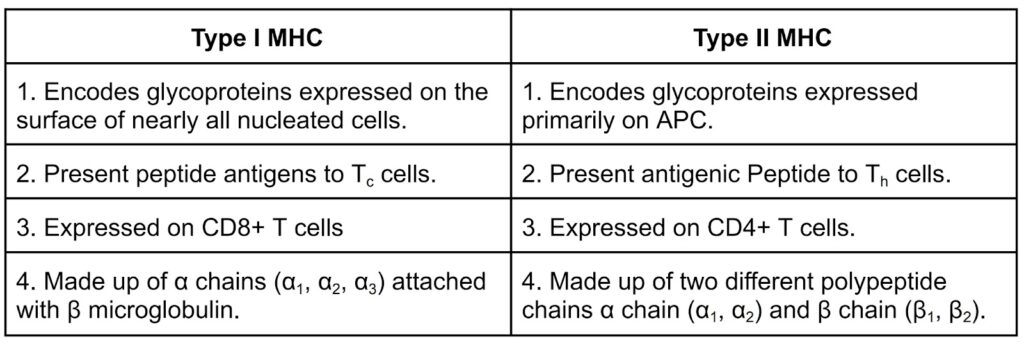
d) What are the basic difference between active and passive immunity.
Ans→

e) How NK cells play a role in innate immunity.
Ans→Kills or destroys the infected cells and cancer cells in the body.
f) What is cytokine pleiotropy? Give an example.
Ans → Cytokine pleiotropy is the ability of a cytokine to exert many different types, many different types of responses, often different target cells.
g) What is opsonization?
Ans→ The process by which a pathogen is marked for phagocytosis is called opsonization.
h) What is the significance of sandwich ELISA?
Ans→ It detects the presence of a target antigen in a sample.
Immunology Paper 2022
a) What is diapedesis?
Ans→ Diapedesis is the movement of White blood cells from the blood vessels towards the site of injury.
b) What is role of histamine?
Ans→ Histamine stimulates gastric acid secretion, plays a role in inflammation and dilates blood vessels.
c) State the significance of hybridoma technology.
Ans→ Hybridoma technology is significant because it produces monoclonal antibodies, which are identical immune cells used in diagnostics, therapeutics, and research.
d) What do you mean by class switching of antibody?
Ans→ Class switching is the process whereby an activated B cell changes its antibody production from IgM to either IgA, IgG, or IgE depending on the functional requirement.
e) What is the role of perforin?
Ans→ Perforin is a glycoprotein chemical responsible for pore formation in the cell membrane of the target cell.
Able to polymerize and form a charmel in the target cell membrane.
f) Which subclass of IgG cannot pass the placenta?
Ans→ IgG 2 subclass.
g) What is the function of mast cell.
Ans→ Mast cells release powerful chemical mediators such as histamine, cytokines, GM-CSF, heparin and many proteases that contribute to homeostasis of the immune system.
i) What is interferon?
Ans→ Interferon are the cytokines that involved in anti-viral infection.
j) What is idiotype?
Ans→ Unique antigenic determinant on the antigen-binding region of an immunoglobulin molecule.
k) What do you mean by monoclonal antibody?
Ans→ Monoclonal antibodies are identical antibodies produced by a single type of immune cell.
l) Give an example of type II hypersensitivity.
Ans→ Blood transfusion reactions, Erythroblastosis foetalis and autoimmune hemolytic anaemia.
m) What is the function of CRP.
Ans→ C- reactive protein (CRP) is an important biomarker of inflammation and infection, helps to identify and respond to infections and other inflammatory conditions.
n) Define autoimmunity?
Ans→ When the immune system can’t recognize the body’s own tissue and attacks the owner’s cells. Then it called autoimmunity.
o) What do you mean by complementarity determining region.
Ans→ Auto Immunity is the system of immune responses of on organism against it’s own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents.
2.a) What is acute phase protein? Give an example.
Ans→ Acute phase proteins are molecules in the blood that increase rapidly during inflammatory responses, helping to detect and respond to infections or tissue damage.
Example: C- reactive protein (CRP)
b) What is colostrum?
Ans→ Colostrum is the primary milk that is secreted by the mammary glands after childbirth which is rich in antibodies (IgA).
c) Differentiate type I and type II MHC.
Ans→
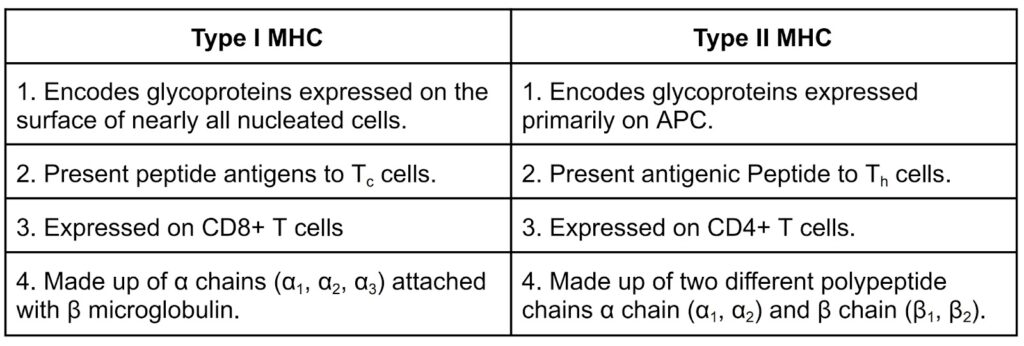
d) “All antigens are not immunogens” – clarify.
Ans→ Immunogen are molecules that are capable of induce an immune response in a body whereas antigens bind to a receptor molecule, it may or may not evoke an immune response. Thus, it can be said that all immunogens are antigens but not all antigens are not immunogens.
e) What are ITAMS?
Ans → ITAMS is a conserved sequence of four amino acids that is repeated twice in the cytoplasmic tails of non-catalytic tyrosine phosphorylated receptors. Cell surface proteins found mainly on immune cells.
f) What is the significance of secretory molecules in IgA?
Ans→ Secretory IgA molecules play a crucial role in mucosal immunity by providing a first line of defence against pathogens at mucosal surfaces, such as the respiratory tract gastrointestinal tracts.
g) What is the basic difference between active and passive immunity?
Ans→ The fundamental difference lies between in how they are acquired and their duration:
Active immunity is acquired by exposure to a pathogen or through vaccination, providing long-lasting protection.
On other hand, Passive immunity is acquired by receiving pre-formed antibodies from another individual or source, providing immediate but temporary protection.
h) State the properties of B cell epitopes.
Ans→ (1) Surface Accessibility: Epitopes should be readily accessible on the surface of antigens for antibody production.
(2) Immunogenicity. They should trigger an immune response, leading to antibody production.
(3) Specificity: Epitopes should be recognized by antibodies, with high specificity.
Immunology Paper 2023
1.a) State the function of IgA.
Ans→ The primary function of IgA is to provide mucosal immunity by preventing pathogens from adhering to mucosal surfaces, such as those in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts.
b) Why does hapten considered as incomplete antigen?
Ans→ Haptens are considered incomplete antigens because they cannot produce any immune response on their own. They need to bind to carrier molecules (such as proteins) to become immunogenic and trigger an immune response. So they are considered as incomplete antigen.
c) What is NK cell?
Ans→ Natural Killer (NK) cells are a type of lymphocyte that plays a crucial role in the innate immune system by identifying and killing virus-infected cells and tumour cells.
d) What is epitope?
Ans→ Epitope is the part of an antigen that binds to an antibody combining site for a specific T cell surface receptor.
e) State the function of Antigen Presenting Cell (APC).
Ans→ The main function of Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs) is to capture, process, and present antigens to T cells, initiating and regulating the adaptive immune response.
f) Name the classical C3 convertase.
Ans→ The classical C3 convertase is the C4b2a.
g) What do you mean by booster dose?
Ans→ A booster dose is an additional dose of a vaccine given after the initial primary series to enhance and prolong the immune response.
h) Which class of antibody is first formed during B-cell development?
Ans→ During B-cell development, the first class of antibody typically formed is IgM.
i) State the characteristics of thymus independent antigens.
Ans→ (i) They are immunogen that can stimulate B cells to synthesize antibodies without the help of T cells.
(ii) These antigens are less complex than thymus dependent antigens.
j) What is TLR?
Ans→TLR or Toll Like Receptors are an important family of receptors that constitute the first line of defence system against microbes. They can recognize both invading pathogen and molecules released from dying cells and damaged tissues.
k) What is an immunogen?
Ans→ Antigen molecules which are able to induce an immune response on the body are called immunogens
l) What is a recombinant vaccine?
Ans→ A recombinant vaccine is a type of vaccine that uses genetically engineered components from a pathogen into another organism, to stimulate an immune response without causing disease.
m) What do you mean by ADCC?
Ans→ ADCC or Antibody dependent, cellular cytotoxicity is a cytotoxic reaction in which the fe receptor bearing Killer cells recognize target cells through/via specific antibodies.
n) What is a type III hypersensitivity reaction?
Ans→ Type III hypersensitivity reactions occur when antigen-antibody complexes form in the bloodstream and deposit in tissues, leading to inflammation and tissue damage. This can cause conditions like autoimmune diseases, serum sickness.
o) What is attenuated vaccine?
Ans→ An attenuated vaccine is a type of vaccine made from weakened or modified forms of pathogens, such as viruses or bacteria, which are still alive but unable to cause disease in healthy individuals.
2.a) State the significance of Membrane Attack Complex (MAC).
Ans→ The Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) plays a significant role in the immune response by forming pores in the membranes of target cells, leading to cell lysis and destruction of pathogens, particularly bacteria and enveloped viruses.
b) Compare opsonization with neutralization.
Ans→ Some differences between Opsonization and Neutralization are
| Points | Opsonization | Neutralization |
| 1. Definition | Opsonization is the process by which pathogens are removed from the system by means of opsonin. | Neutralization is the process of neutralizing the effect of antigen by neutralizing antibodies. |
| 2. Type of molecules involved | Opsonins | Neutralizing antibodies |
| 3. Type of immunity involved | Both adaptive and innate immunity | Adaptive immunity |
| 4. Function | Increases the efficiency of pathogen clearance from the body by phagocytosis. | Provides protection by directly neutralizing the pathogen without involving phagocytosis. |
c) Differentiate between idiotype and allotype.
Ans→ Some differences between idiotype and allotype are :
| Points | Idiotype | Allotype |
| 1. Definition | Unique antigenic determinants found in the variable region of an antibody. | Genetic variations found in the constant region of antibodies within a species. |
| 2. Location | Located in the variable regions of the heavy and light chains. | Located in the constant regions of the heavy and light chains. |
| 3. Specificity | Determines the specificity of the antibody for its particular antigen. | Does not affect antigen-binding specificity. |
| 4. Function | Involved in antigen recognition and binding. | Mainly structural; reflects genetic differences between individuals. |
d) What are monoclonal antibodies?
Ans→ Monoclonal antibodies are identical antibodies produced by a single type of immune cell.
e) State the salient features of adaptive immunity.
Ans→ Each adaptive immune cell has a specific receptor.
Each receptor recognizes an antigen which is onto any molecule that may bind TCR.
f) State the properties of T-cell epitopes.
Ans→
- Peptide Sequence: They are typically short peptide sequences, usually 8 to 12 amino acids long.
- MHC Binding: They bind to MHC molecules, on the surface of antigen-presenting cells.
- Recognition: T-cell epitopes are recognized by T-cell receptors (TCRs) on the surface of T cells, leading to T-cell activation and immune response.
g) What is opsonization?
Ans→ The process by which a pathogen is marked for phagocytosis is called opsonization.
h) Describe the concept of clonal selection.
Ans→ Clonal selection is a theory of naive lymphocytes entering the bloodstream, only those exposed by binding antigen on the receptor are able to stimulate to proliferate into effector cells. Upon binding The antigen Lymphocytes become activated and divide and make clones of

Very helpful 👌 thank you for providing PYQs answers also. ❤️
A very helpful website
Very helpful for us👌