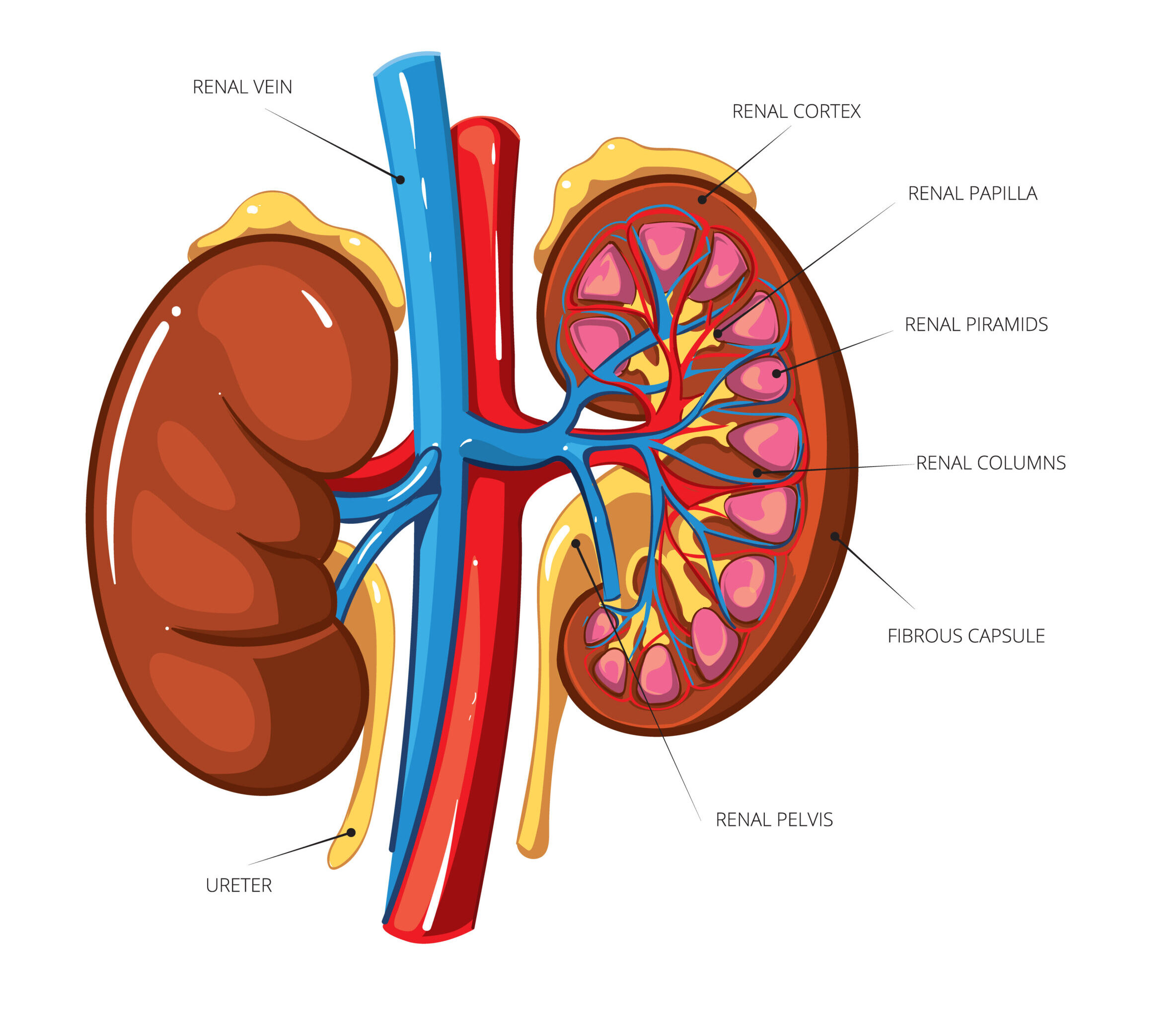
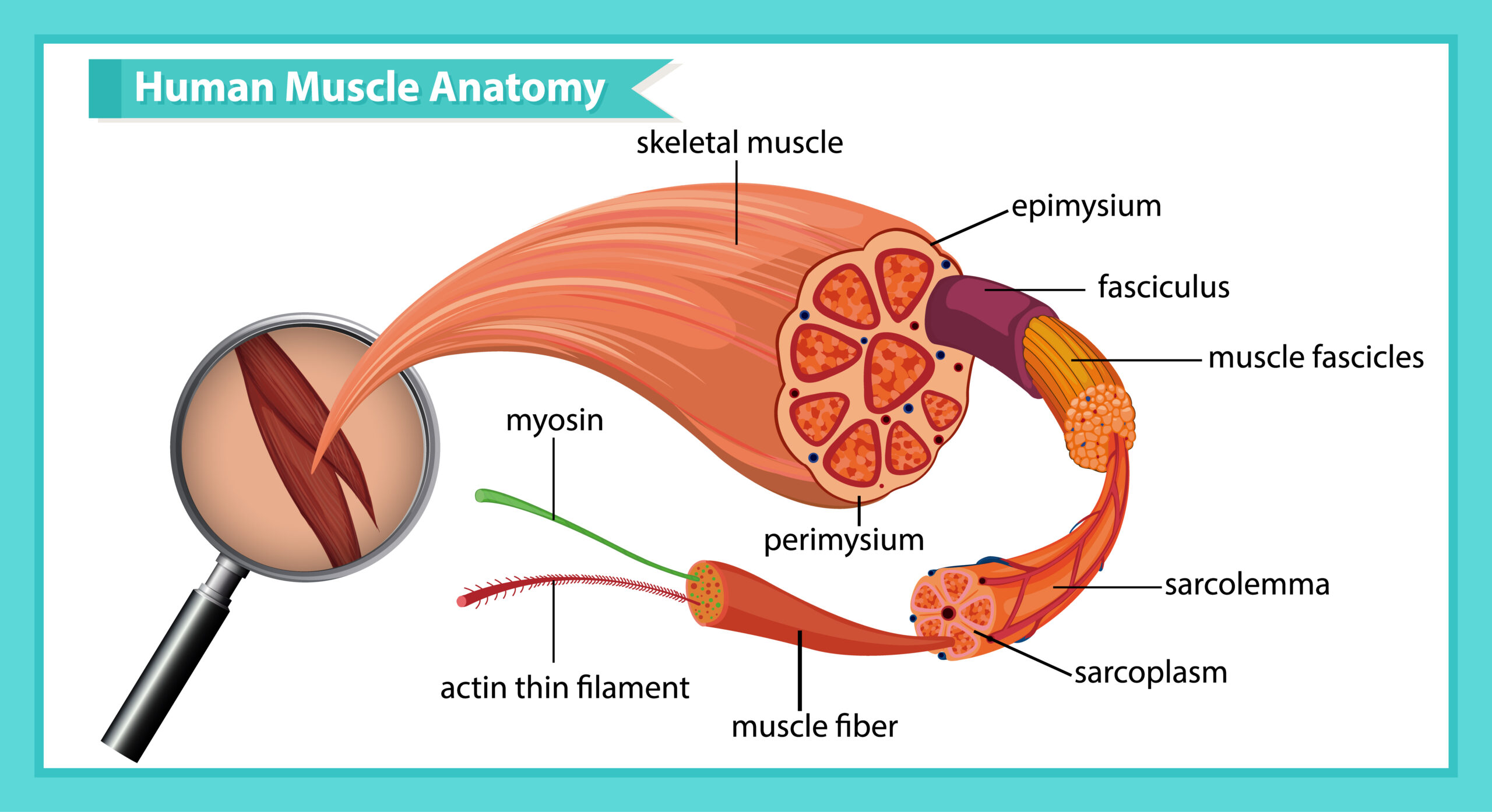
Endocrine Glands: Hormones and their Regulations
Endocrine glands are specialized organs that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones regulate various physiological processes, including growth, metabolism, and mood. Unlike exocrine glands, which release substances through ducts, endocrine glands are ductless. Key endocrine glands include the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal glands, and the pancreas. Each gland produces specific hormones, such as insulin … Read more